The Advantages of a Flying Point of view — How Robots are Changing the Agrarian Business Leave a comment
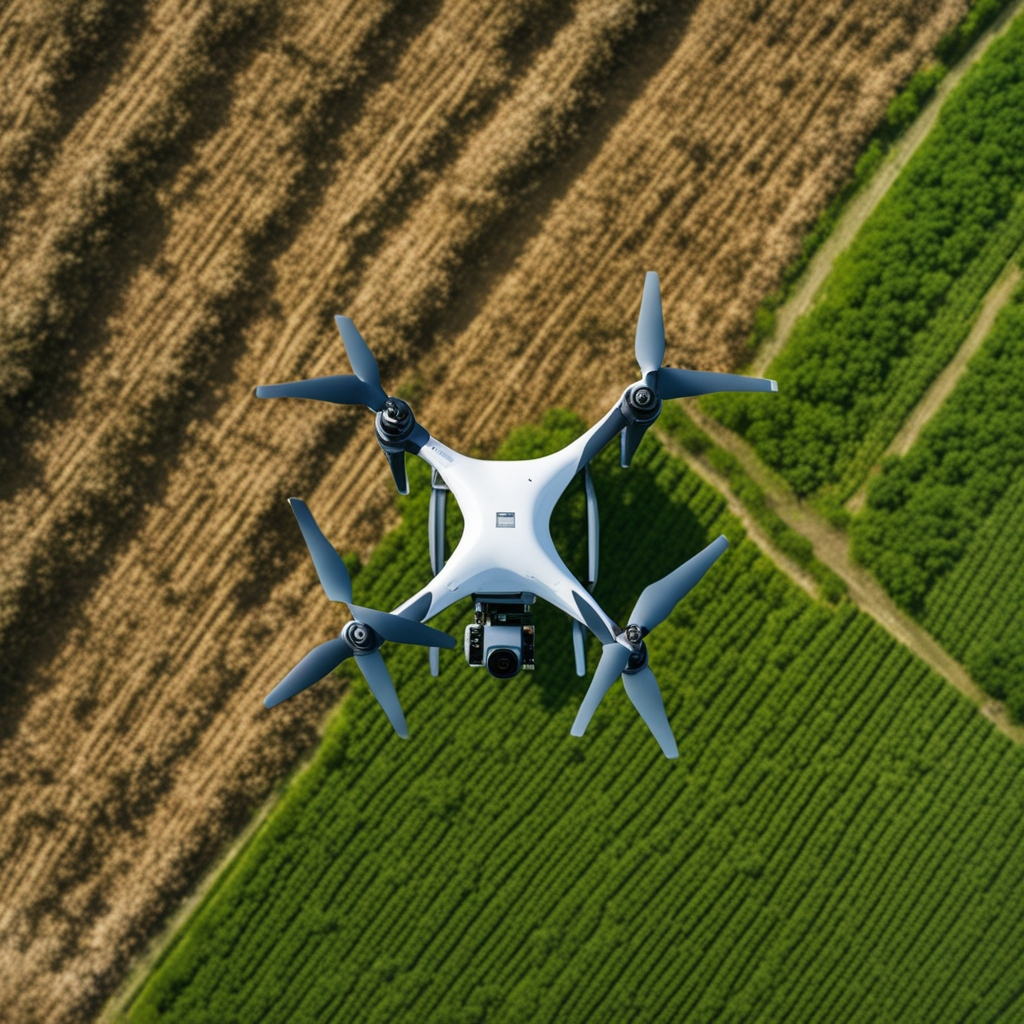
In the agricultural heartlands, a distress is taking off — not with the roar of ranch haulers, yet rather with the mumble of robots. The cost relationship alone is wavering — a strong moderate measured ranch vehicle passes through the bank at $500,000, while a robot, offering a comparative work, floats at a to some degree genuine $150,000. Be that as it may, for Jim Fry, a sixth period farmer with soil in his veins and the future in his sights, the leap from diesel-gulping behemoth to the robot is tied in with something past monetary issues. It’s a principled surprise; less outpourings, less soil compaction that smothers crop centrality, and an exactness in shower application that is laser-sharp conversely, with the old, eccentric techniques. In this new time of cultivating, drones are not just gadgets for contemplating; they are the vanguard of a developing turn of events, changing the rulebook on efficiency and viability from a raising vantage point. Singe’s change is a showing of this epochal shift — where the buzz of robot propellers cutting through the air declares a cleaner, greener, and more copious harvest season.
Examining a robot’s actual limit
Mechanized raised structures, moreover called drones, can be altered for various purposes in the plant business. This integrates land imaging, soil noticing, gathering soil and water tests, surveying geography and cutoff points, and researching — to give a few models. Robots can also be used by ranchers to monitor animal and yield conditions from a distance and without going through the actual field. Other than the way that this save times, yet can consider various purposes to turn out to be conceivably the main component — , for instance, with respect to fertilizer and pesticide application.
A multispectral camera can work “to quantify close infrared reflectance to evaluate the soundness of the singular plant,” while photogrammetry and GPS, for example, can enable a robot to make a map of a field and precisely locate each plant. Such data can be used for fertilizer applications, as demonstrated by Michael Nattrass, partner instructor of agronomy and soils at Particular school’s of Cultivating, really allowing producers to expand the capability of manure application while decreasing the aggregate applied. However, the benefits of using robots can go much further; Nattrass mentions that they may be useful for increased pesticide applications, which may attempt to further develop maintainability. I get so empowered examining drones since I acknowledge they will expect a fundamental part descending the line for agribusiness, from harvests to steers,” Nattrass said.
The case for extended prosperity
Close by the numerous organizations that robots can give, prosperity is a critical benefit — especially with respect to the dangers of the gig. Irrefutably the most unsafe situations in the country incorporate occupations, for instance, improvement that are essentially risky on account of their propensity. On a construction site, a number of injuries and mishaps can occur, including falls, trips, and the risk of being struck by a falling object. Working in cultivating is something very similar, with the possibility of the gig suggesting risks, for instance, pesticide receptiveness and setbacks including contraption. Truly, work vehicle rollovers are the fundamental wellspring of fatalities in the business, addressing most of all farm related passings, includes the School of Missouri Extension. To extra underline the gamble, one of each and every 10 work vehicle overseers disturbs a ranch truck throughout their life. In addition, the U.S. Department of Labor’s Work Measurements indicates that for every 100,000 horticultural workers, there are 23 business-related deaths, which is a rate that is multiple times higher than the general norm for laborers. Utilizing robots, on the other hand, can assist in limiting pesticide openness by allowing ranchers to remotely splash, and it can also enable ranchers to observe crops without having to leave the work vehicle.
Authentic models
With the extended inescapability of robot use, there are a couple of drives and veritable models that are endeavoring to extra element inventive purposes for the development inside the cultivating region. An advancement organizations association by the name of Taranis is only one very critical. Depicting its primary objective as giving “A.I. controlled crop information courses of action,” Forbes saw that the association is including mind boggling and pragmatic robot advancement to gather season-long pictures of creating harvests. As shown by Forbes, Taranis accumulates photos of each contracted field every 10 to 12 days, amounting to six passes for each season. The photos feature sub-millimeter objective, achieving amazing nuances. ” They can be caused by insect infestations, weed attacks, deficiencies in crop supplements, stress, or a variety of other beneficial or unfavorable changes on the ground, Forbes explains. Beginning around 2022, Taranis checking was conveyed on 3,000,000 segments of place that is known for farmland, and they at present have an association of numerous directors by working with the gig-economy area of free robot controlling.
Drone use in country settings can in like manner be found in Moldova, where such robots are logically used by farmers. With the help of robots, DRON Help (an association that is financially maintained by UNDP Moldova and the European Affiliation) offers sharp sorts of help to Moldovan farmers — including vermin and weed organization as well as the preparation and seeing of rustic land. In the town of Onitcani, for example, a major piece of a wheat field (of 73 ha) will be treated with herbicides using a robot while the other is done with the use of a sprinkler and homestead truck. Growing the advantage of yields is in a general sense significant, hence the experimentation. ” We really want to make an assessment. We treated the corn plant seeds last year, and the results were perfect. That’s why we’re trying the wheat field this year, “explains head Alexandru Zolotco.
The use of robots in a provincial setting can bring different benefits, from the more viable utilization of pesticides and fertilizer to arranging and really taking a look at farmland. As a result, the innovation has the potential to not only improve aspects like workplace security but also effectiveness.